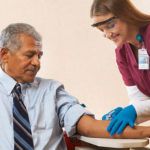
A phlebotomist is a clinical support worker that collects blood samples from patients. They specialized in drawing blood from patients, usually through a vein — a procedure known as a venipuncture. Blood samples are then sent for medical testing, transfusions, or research.
Certified phlebotomist perform a variety of invasive medical tasks, keep track of laboratory records, and ensure proper all-round functioning of the clinic. They interact with patients and guide them through procedures.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, phlebotomy technician jobs are expected to increase by up to 25% until 2026. The average American medical phlebotomist has a high school diploma or GED and an annual salary of $33,670 or roughly $15.50 an hour.
Personality Type
The ideal phlebotomist is, first of all, a people person. Having to deal with patients who might be unstable emotionally or physically while figuring out the best solution. Second of all, the worker has to have a natural inclination towards the scientific approach. Most clinical operations require precise measurement and protocol.
Skillset
Soft Skills
- Stamina. Long and stressful hours are possible in some instances, such as national emergencies;
- Detail-oriented. Attentiveness towards details such as labeling, prescriptions, and so on is imperative;
- Multitasking. The ability to focus on multiple duties is essential in ambulatory settings;
- Social skills. Maintaining an emphatic mindset when dealing with different patients is vital;
- Good memory. Remembering patients by name and face, as well as other information, can prove helpful.
Hard Skills
- Communication. Whether with patients or staff, a clear dialog is critical;
- Languages. Knowledge of other languages, such as Spanish is an advantage;
- Dexterity. Good hand-eye coordination and a steady hand are obligatory;
- Organizational skills. Maintaining transparent bureaucracy and administration makes work easier;
- Digital skills. Basic computer knowledge and familiarity with medical software are required.
Job Requirements
- Venipuncture, capillary sampling, peripheral I.V.s;
- Aseptic procedures, sutures replacement, and specimens gathering;
- Bio hazardous material labeling and disposal;
- Patient identification and registration;
- On-site technical and social problem-solving;
- Law and privacy knowledge of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) confidentiality procedures.
Education and Training
The average phlebotomy technician has a high school diploma, equivalent GED, or post secondary school. They have also pursued certification from recognized agencies. As previously mentioned, likewise for the case of general certified medical assistants, formal education is not always legally required. However, employers strongly prefer candidates with proper documentation from reputable certifying entities. It ensures that the medical worker is adequately trained and represented throughout their career. Lowering the chances of malpractice and safeguarding them against litigious actions.
Theoretically, some states might allow a high school graduate to work in the healthcare system with just hands-on training at the job site. Assuming the employer would be willing the take the risk of such an approach, the worker could indeed shortcut training time while even getting paid. However, such an unorthodox method creates legal vulnerabilities. Constitutionally, patients have their rights reserved to sue medical practitioners. And because of the judicial nature of the healthcare industry, uncertified workers are at a net disadvantage.
Most importantly, some states don’t even accept untrained or uncertified phlebotomy technicians. For example, Washington, California, Louisiana, and Nevada require special state certification. And although certification can be obtained through several different organizations, California accepts only six certification boards:
- National Center for Competency Testing (NCCT) or Multi-skilled Medical Certification Institute (MMCI);
- American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP);
- American Medical Technologists (AMT);
- American Certification Agency (ACA);
- National Healthcareer Association (NHA);
- National Credentialing Agency (NCA).
Which phlebotomy certification is best?
It could be argued that the six boarding institutions mentioned above are the best in terms of universality as they allow to work wherever in the United States, including stricter California. Other highly respectable & nationally recognized institutions that certify across the United States include:
7. National Phlebotomy Solution (NPS) at 866-319-7052 for $150 (Exams & Study Materials)
8. American Society of Phlebotomy Technicians (ASPT) at 828-294-0078 for $85 (Exam Only)
9. National Phlebotomy Association (NPA) at 301-386-4200 for $130 (Exam Only)
10. American Association of Bioanalysts (ABOR) at 314-241-1445 for $90 (Exam Only)
11. American Allied Health (AAH) at 479-553-7614 for $105 (Exam Only)
12. American Medical Certification Association (AMCA) at 888-960-2622 for $109 (Exam Only)
Certification
CPT & Other Equivalent Acronyms
Many certification boards are releasing phlebotomy degrees under various acronyms such as Certified Phlebotomy Technician (CPT), Registered Phlebotomy Technician (RPT), Phlebotomy Technician (PBT), National Certified Phlebotomy Technician, and so on. Although the certificates are distinct from one another, they hold a basic equivalency in the health industry.
What is the difference between phlebotomist and phlebotomy technician?
Employers require official certification for hiring but tend to not discern between the private licensing boards. Nevertheless, employers do differentiate between job posts based on individual certifications. For example, a phlebotomy technician might restrict their duties to laboratory work, while a phlebotomist will both draw blood and perform lab work.
1. National Center for Competency Testing (NCCT) or Multi-skilled Medical Certification Institute (MMCI):
The Phlebotomy Technician (PBT) accreditation doesn’t have online exams and costs between $90 and $135. Recertification is required annually for a $77 fee. Candidates must have a high school diploma or equivalent GED. Eligibility is as follows:
- Route 1A for current students who completed a phlebotomy technician certification for a test fee of $90;
- Route 1B for graduates from an NCCT authorized institution within the past five years. The cost is $90 but increases to $135 if the exam is taken after six months of graduation;
- Route 2 for experienced full-time phlebotomy health care practitioners who have one year of verifiable employment (2080 hours) within the past five years for an exam fee of $135;
- Route 3 for military personnel who has terminated formal medical training relating to phlebotomy for an exam fee of $90.
More about the program can be found on the official NCCT/MMCI website. Check for approved test sites at 800-875-4404.
2. American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP):
The Phlebotomy Technician (PBT) certification by the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP) costs $135. The tests are not available online, and the re-certification fee is $100. Eligibility is reserved for high school graduates who qualify for at least one of the seven routes:
- Route 1 has completed a National Accrediting Agency for Clinical Laboratory Sciences (NAACLS) approved phlebotomy program within the last five years;
- Route 2 has finished a two-part phlebotomy program within the previous five years consisting of 40 hours of classroom and laboratory training, specimen collection, processing, and handling, and 100 successful unaided venipunctures;
- Route 3 has worked full time in an acceptable clinical environment for one year as a phlebotomy technician within the last five years. Must include having done venipunctures and skin punctures;
- Route 4 has completed a Registered Nurse (RN), Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN), or other accredited allied health education with a minimum of 100 unaided venipunctures and skin punctures;
- Route 5 owns a valid Medical Laboratory Scientist (MLS)/Medical Technologist (M.T.) certificate or a Medical Laboratory Technician certificate;
- Route 6 has a legitimate Donor Phlebotomy Technician (DPT) certification and 100 registered successful unaided non-donor venipunctures and skin punctures within five years;
- Route 7 has graduated from an approved phlebotomy certification program by the California Department of Public Health within five years.
More about the program can be found on the official ASCP website. Check for approved test sites in the U.S. and Canada at 312-541-4999.
3. American Medical Technologists (AMT):
The Phlebotomy Technician (RPT) award by the American Medical Technologists (AMT) is reserved for high school graduates who are finishing a phlebotomy training program with a minimum of 120 educational hours or graduates within four years from a formal phlebotomy technician program with a minimum of 120 didactic hours. Eligibility is also given to those with a minimum of 1,040 hours of work experience as a phlebotomy technician in the past three years. The technician certification exam costs $100 and requires an annual re-certification fee of $60. Online exams are available.
More about the program can be found on the official AMT website. Check for approved test sites at 800-275-1268.
4. American Certification Agency for Healthcare Professionals (ACA):
The ACA certification test requires a high school diploma or GED. The application fee costs $100.
To become an ACA certified phlebotomist, applicants must have one year of working health care experience involving phlebotomy skills, completed an official phlebotomy program, or have a degree from an ACA approved patient care program. Recertification is required by continuing education. A two-year renewal costs $80. Ineligible candidates will be refunded the exam fee minus a $35 processing fee.
More about the program can be found on the official ACA website. Check for approved exam sites at 574-277-4538.
5. National Healthcareer Association (NHA):
The Phlebotomy Technician Certification (CPT) award from the National Healthcareer Association (NHA) costs $115. It consists of 20 pretest questions, 100 exam questions in two hours at a validated school or local PSI Testing Center. Recertification is required every two years for a fee of $169. Eligible candidates must have a minimum of 30 venipunctures and ten capillary stick procedures. They also have to have completed an NHA approved certification, military training, or supervised health care experience.
More about the program can be found on the official NHA website. Check for approved test sites at 800-499-9092.
6. National Credentialing Agency (NCA):
The National Accrediting Agency for Clinical Laboratory Sciences (NAACLS) or National Credentialing Agency (NCA) is an accrediting board with approved schools and facilities across the United States. It provides full certified phlebotomist courses. The agency works through many schools, universities, and campuses, which are approved by its board of professionals.
More about the accredited institutions can be found on the official NAACLS/NCA website. Check for approved test sites at 773-714-8880.
7. National Phlebotomy Solutions (NPS):
National Phlebotomy Solutions (NPS) offers certification at the cost of $150. It includes study materials, unlimited simulations, and three final exam attempts. Because of the unique online testing method with three final exam attempts, the NPS curriculum has one of the highest compatibility rates in the market. More so, the candidate has no time limit to study or practice before the exam.
NPS is a member of the Institute for Credentialing Excellence (ICE) and has a job placement assistance initiative.
NPS is nationally accredited by P.A.C.E through the American Society of Clinical Laboratory Sciences. Certification renewal is required every two years for a $150 fee.
More about the program can be found on the official NPS website page for Certified Phlebotomy Technician Certification. More information at 866-319-7052.
Scams
Phlebotomists be aware, there are websites online pretending to provide phlebotomy certification 100% online. Some are major players that we have all heard of before. This is not possible. They can provide you the educational aspect, but you must receive hands on practical experience to qualify for a national certification.
*Due to COVID-19, many agencies began allowing a grace period on providing documentation of having met the prerequisites. This does not negate your responsibility to ensure you meet the requirements. Your certification may be suspended if you do not provide documentation, and employers may be held accountable.
Known Scams
National Phlebotomy Credentialing Excellence (NPCE)
OR
National Phlebotomy Credentialing Examination (NPCE)
NPCE.org offers Phlebotomy & EKG Certifications on their website. NPCE offers all of the same programs a real agency would, and always have the best price. The business appears to be a professional agency at glance. NPCE.org provides all of their study materials & exams online. They use this elaborate scheme to charge people for certifications that are not accepted, and are not nationally recognized.
NPCE states to be the only California approved Phlebotomy program in multiple places online. California does not recognize nor accept NPCE certifications, nor as a provider of Continuing Education in any capacity.
NPCE.org has been barred by every credentialing agency within the medical community. There have been numerous complaints filed against the company that go back to 2011. Phlebotomists beware.
Salary
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics estimated an annual salary of $33,670 or roughly $15.50 an hour for phlebotomy technicians in 2018. Virtually the same retribution as the average salary of a Certified Medical Assistant.
The two most important independent factors when talking about salary range are job typology and geographic location. According to PayScale.com, the highest salaries at around $26 per hour are most common in California, Washington, Colorado, Idaho, Nevada, and New Mexico. An average rate of $18 per hour is most common in New York, Vermont, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island. On the other hand, the lowest prices at $8 per hour are typical of Louisiana, Texas, and Arkansas. Qualification is also a determining pay factor. For example, a PSC site collector or a blood donor technician is expected to earn between $15 and $14, while a lab assistant, technician, or a mobile phlebotomist are paid at $12 per hour.