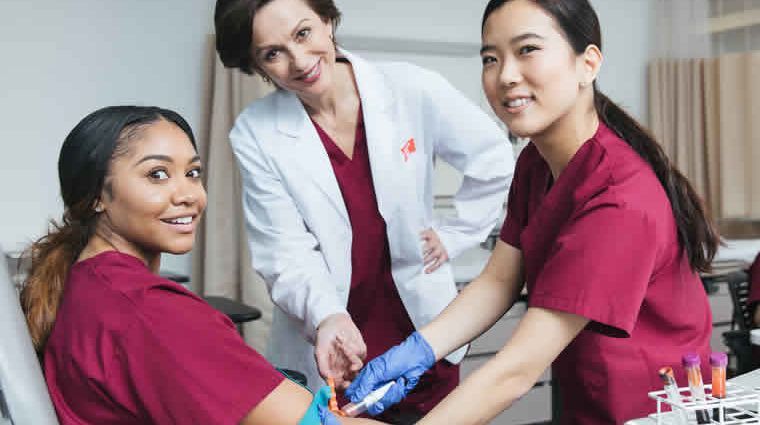
A Certified Medical Assistant is a clinic employee who support doctors in their clinical duties. They are the right hand of the medical practitioner and make sure the patient visits run smoothly.
More precisely, the medical assistant divides their labor into administrative work and ambulatory tasks delegated by the medical provider such as preparation work, client debriefing, performing diagnostics, sterilization, and hazardous material disposal.
What does CMA stand for?
CMA stands for Certified Medical Assistant. It refers to an individual who has been approved by the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA) certifying board.
The typical medical assistant in the field has completed a one year program or a more specialized two-year associate’s degree. The average one-year diploma or certificate can put the health care professional in the vicinity of a yearly salary of $33,610.
Personality Type
What is a medical assistant like?
Clinical medical assistants must possess personality traits, such as:
- Patience. Clinical medical assistants must have patience with individuals who may be tired, anxious, frustrated, and ill;
- Conscientiousness. Medical support professionals need to have a natural desire to accomplish their duty well and thoroughly;
- Compassion. Clinical medical assistants need to have an innate desire to help others who are in need;
- Empathy. Medical assistants must be able to listen and understand their patients’ emotions, specifically with individuals who suffer from diseases or mental illnesses;
- Sociability. Clinical assistants must be able to communicate easily with colleagues, patients, and superintendents;
- Self-control. Medical support professionals need to control themselves emotionally, especially in difficult and stressful situations. They need to have stable mental fitness against stress, phobias, and fatigue.
Skillset
Soft Skills
So, what is a CMA’s skill set? The job of CMA includes dealing with technology and bureaucracy; therefore, they need to know administrative, social, and managerial skills such as:
- Multi-tasking. Medical assisting professionals need to remain professional, on-task, and organized;
- Attentiveness. Certified medical assistants have to pay close attention to detail, especially when taking vital signs or recording patient information;
- Communication. Clinical assistants need to be able to communicate with colleagues and patients easily.
- Organizational skills. Medical assisting professionals have to be able to manage and update patient records and appointments, as well as managing the clinic’s mail traffic and inventory;
- Bureaucratic skills. Medical assisting workers need to be savvy in processing insurance forms, performing general office accounting, billing, and credit arrangements. They must also possess knowledge in federal and state regulations, office policy, and procedure manual;
- Digital skills. Clinical medical assistants need to be knowledgeable in medical accounting procedures, industry software applications, healthcare coding, financial statements, cost analysis, and budgeting.
- Language skills. The clinical assistant has to understand medical terminology, abbreviations, and symbols used in the medical office;
Hard Skills
Medical assistant duties revolve around analytical and technical skills. To be successful in the business, the following are necessary:
- Ability to use clinical instruments to take a patient’s vital signs, such as heart rate and blood pressure;
- Familiarity with the anatomy and physiology of the human body;
- Dexterity to perform sensible physical operations with a stable hand. Such as phlebotomy, venipuncture, and capillary sampling (drawing blood). Peripheral IVs, aseptic techniques, infection prevention, and changing sutures and dressings.
- Preparation knowledge to set up the clinical setting;
- Disposal awareness to safely discard dangerous and bio hazardous material;
- Good memory is needed around the clock to ensure correct paperwork, pharmaceutical prescriptions, and diets.
Some of the fundamental medical assisting skills include:
- Being able to understand and follow medical charts and diagnoses;
- Understanding medical terminology as well as EKG function and EKG strip analysis.
Clinical medical assistants need to:
- Have an awareness of the legal aspects of medical assisting;
- Keep patient information private in conformity with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) confidentiality procedures.
Job Requirements
What does a medical assistant do? Well, some of the essential medical assistant requirements include:
- Administration, office procedures, bookkeeping, insurance processing;
- Patient records registration, medical coding, and appointment scheduling;
- Clinic tasks, such as sterilization, specimen gathering, and, diagnostics;
- Communication with staff and patients.
Education and Training
Candidates should have a high-school diploma, a GED equivalency degree, or post secondary school.
Those with a high school diploma or an equivalency degree, such as the GED’s Certificate of High School Equivalency, can enter the workforce with just on-the-job training. However, finding a practitioner that would hire a non-trained CMA can be challenging.
Prospects can obtain a postsecondary school certificate by attending medical programs at local colleges or universities. It generally takes 9 to 12 months to geta certified or 18 to 24 months to get an associate’s degree.
Can you take the medical assistant exam without going to school?
The programs offer certification upon taking classes online, on campus, or a combination of the two. Some certifying degrees can be obtained by taking only virtual classes.
Best is to make sure they’re CAAHEP (Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs), or ABHES (Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools) approved to retain validity for future medical assisting business opportunities and continuing education.
Clinical training includes, but not limited to:
- Human anatomy, physiology, and pathology;
- Medical terminology;
- Laboratory techniques;
- Clinical and diagnostic procedures;
- Pharmacology and medication administration;
- Patient relations and interpersonal communication;
- General administrative and clinical office practices;
- First aid;
- Keyboarding and computer applications;
- Recordkeeping and accounting;
- Coding and insurance processing;
- Medical law and ethics.
Certification
CMA\CCMA\Other Equivalent Acronyms
A few governing bodies and medical associations are releasing certifications for those wishing to enter the U.S. health care. The most known certifications include:
- Certified Medical Assistant or CMA awarded by the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA);
- Certified Clinical Medical Assistant or CCMA available from the National Healthcareer Association (NHA);
- Certified Medical Administrative Assistant or CMAA released by the National Healthcareer Association (NHA);
- National Certified Medical Assistant or NCMA from the National Center for Competency Testing (NCCT);
- Registered Medical Assistant or RMA within American Medical Technologists (AMT);
- Clinical Medical Assistant Certification, Phlebotomy Technician Certification, and Electrocardiograph (EKG) Technician Certification or CMAC/PTC/ETC obtainable from the American Medical Certification Association (AMCA).
So what is the difference between a certified medical assistant and a medical assistant?
Although there’s no legal requirement to get certified or licensed to work, employers have a firm preference for candidates with medical certification. Moreso, it has become a de-facto standard for employment. Due to the litigious nature of the industry, clinics need well-trained professionals who are guaranteed by renowned certifying entities.
Having formal training and certification makes it safer for every party involved: the medical assistant, the doctor, and the client. Certified medical assistants have standardized practices, greater familiarity with laws and bureaucracy, added work experience, access to Medicaid EHR Incentive Program, get better legal representation, and business opportunities.
Uncertified assistants cannot advertise themselves by using trademarked words or phrases such as “CMA,” “CCMA,” or “Certified.” Doing so could result in legal problems.
1) The Certified Medical Assistant or CMA exam from the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA) is available year-round, nationwide. It consists of 200 multiple-choice questions in 40-minute intervals. It costs $125 for AAMA members, $250 for non-members.
Furthermore, re-certification is required every 60 months through re-examination or continuing education by scoring a minimal number of points. The cost of reactivation is $50 plus additional exam fees.
The CMA credential is the only degree program that requires post-secondary promotion from schools sanctioned by the United States Department of Education (USDE) or the Council for Higher Education Accreditation (CHEA).
An eligible candidate is also a medical assisting program graduate from the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) or the Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools (ABHES). This publicly-recorded certificate is one of the most valid documentation on the market.
More about the program can be found on the official PDF guide. Check for approved exam sites at 800/228-2262.
2) The Certified Clinical Medical Assistant or CCMA exam from the National Healthcareer Association (NHA) is composed out of 30 pretest questions, 150 questions, and three hours to complete. It costs $155, at a PSI Testing Center or approved school.
The CCMA remains active for two years. After the period, certified medical assistants need to pay renewal fees and decide on continuing education. The CCMA certification offers a very comparable position to that of the CMA.
More about the program can be found on the official PDF guide. Check for approved exam sites at (800) 499-9092.
What is the difference between a CMA & CCMA?
The main dissimilarity is that the CMA worker has been validated by a different certifying board than a CCMA worker in the same position. However, the CMA certification has somewhat stricter medical assistant education requirements. Mainly, the added condition of the CAAHEP or ABHES accreditation. Also, The CMA certification does not accept felons. On the other hand, the CCMA certification can be pursued directly, but only if the school is NHA approved.
3) The Certified Medical Administrative Assistant or CMAA exam from the National Healthcareer Association (NHA) consists of 20 pretest items, 110 questions, and 2 hours and 10 minutes to finish it. Tests are held at a PSI Testing Center or approved school, and costs $117.
The position offered by the certification, also known as Medical Office Secretary or Medical Office Assistant, is centered around management and administration. Usually, the CMAA medical assistant will have excellent secretary skills and run health care offices by operating computer systems and managing bureaucracy.
More about the program can be found on the official PDF guide. Check for approved exam sites at (800) 499-9092.
4) The National Certified Medical Assistant or NCMA exam from the National Center for Competency Testing (NCCT) consists of 150 scored test items in 3 hours. The test is held at an NCCT authorized school.
Eligibility for the test comes in three possibilities: for students and graduates, experienced workers, or military personnel.
- Route 1A for current students, graduates, or equivalent credential holders (e.g., GED) for an exam fee of $90.
- Route 1B for graduates from a Medical Assistant program at an NCCT authorized school in the past five years. The cost of the exam is $90 for those who take the test within six months of graduation. Or $135 for those who take the test after six months.
- Route 2 for experienced assistants with a minimum of 2 years experience (4160 hours) as a certified medical assistant CMA within the past five years for an exam fee of $135.
- Route 3 for military personnel who has completed formal medical assistant training or equivalent during the service within the past five years. Available for military personnel, or a spouse thereof, who has a minimum of two years of experience as a medical assistant practitioner within five years. Keep in mind that instructors are not equivalent to practitioners.
More about the program can be found on the official PDF guide. Check for approved exam sites at 800-875-4404.
RMA
5) The Registered Medical Assistant or RMA credential exam from the American Medical Technologists (AMT) costs $120 and has an annual fee of $60.
Eligibility for the exam is reserved for:
- Recent medical assisting program graduates within four years;
- Military personnel graduates within four years from a medical training program in the Armed Forces;
- Workers who are high school graduates and have been employed full-time as certified medical assistants in five out of the last seven years;
- Instructors with at least five years of working experience in health care;
- Individuals who have passed an exam from another certification body approved by the AMT Board of Directors.
More about the program can be found on the official PDF guide. Check for approved exam sites at 847.823.5169.
ETC
6) Clinical Medical Assistant Certification, Phlebotomy Technician Certification, and Electrocardiograph (EKG) Technician Certification or CMAC/PTC/ETC exam cost a total of $169.
There are two parts of the test: the CMAC test and the PTC/ETC exam. The first part includes 200 inquiries in 3 hours and 15 minutes to complete, while the second part carries 50 questions in one hour.
More about the program can be found on the official PDF guide. Check for approved exam sites by calling 888.960.AMCA(2622)
Salary
According to the Bureau of Statistics, the annual wage for certified medical assistants is $33,610 ($16.16 per hour). The job outlook for the near future is expected to grow by 23%.
The geographic region affects the salaries range, as reported by a 2013 American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA) survey. New England and The Pacific region of the United States have reported the highest salaries:
- Pacific: $33,322 per year ($17.60 per hour);
- New England: $30,997 per year ($15.93 per hour);
- Middle Atlantic: $29,756 per year ($15.22 per hour);
- East North Central: $28,614 per year ($14.67 per hour);
- West North Central: $30,871 per year ($16.15 per hour);
- South Atlantic: $28,619 per year ($14.54 per hour);
- East South Central: $28,712 per year ($14.13 per hour);
- West South Central: $30,450 per year ($14.75 per hour);
- Mountain: $30,208 per year ($15.06 per hour).