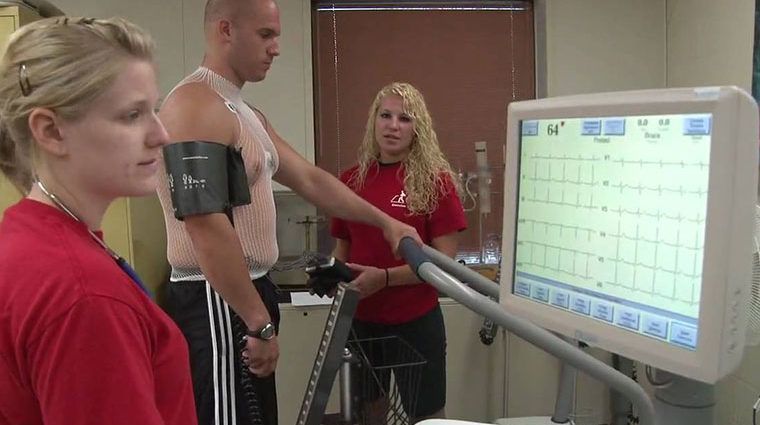
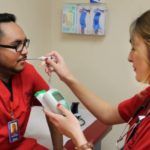
An electrocardiograph technician (also known as electrocardiogram technician) is a certified cardiovascular specialist who observes the patient’s heart performance by using wires and electrodes.
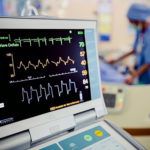
The EKG machine outlines electrical impulses sent by the heart through electrodes connected to the patient’s arms, chest, and legs. It prints an activity graphic for the interpretation of the medical practitioner before or after a routine examination or surgery.
The electrocardiograph technician makes sure the machine is working correctly, guides the patient through the procedures, performs stress testing, and documents the readings. EKG techs are high school graduates who pursued certification and training.
A typical CET certified EKG technician has an average salary of $56,850 ($27.33 per hour).
Personality Type
An ideal certified EKG technician is an emphatic professional with excellent attention to detail. They possess an innate understanding of graphics and numbers, with exceptional written and verbal communication. Moreover, the EKG technician must have stamina and a natural tendency towards physical activity. The technician must be able to handle stress and be resilient, as some situations may require longer hours or additional human resources. Also, having some sports and nutrition expertise may prove useful in understanding the cardiovascular system better.
Skillset
Soft Skills
- Attention to detail. Certified EKG technicians must be precise and have a good eye for the subtleties of the job.
- Empathy. In order to smoothly guide the patient through medical processes, the EKG technician must be able to maintain a calm and reassuring environment.
- Curiosity and intuition. The EKG technician must have the willingness to investigate the patient’s situation and formulate possible solutions.
- Stamina. Both physical and mental strength is required, as the job can be fatiguing and stressful. The health care technician must be able to lift heavy machinery and walk thousands of steps every day.
- Multi-tasking. Performing multiple concurrent tasks is not uncommon. An ideal EKG technician also has a good memory.
- Communication. The EKG technician must be able to communicate with staff and patients efficiently.
Hard Skills
- Mathematical skills. The EKG technician must be able to read EKG graphs and values correctly.
- Computer skills. Registering various data requires having basic medical software knowledge.
- Organization. The EKG certified health care worker must maintain a clean and tidy clinic for a productive workplace.
- Vocabulary. An EKG technician CET must have knowledge of job-specific terminology.
- Dexterity. Handling sensible pieces of equipment requires good hand-to-eye coordination and a steady hand.
- Chemistry and biology. The technician must be knowledgeable about anatomy and physiology.
- Pharmaceutical expertise. Knowing the standard drugs and dosages is vital in treating patients.
- Bureaucratic skills. Medical technicians will often need to process insurance, billings, and other documents.
- Foreign languages. Knowing other languages, such as Spanish, may prove useful when treating international patients.
Job Requirements
The EKG technician must have a high school diploma or GED, and at least one official certification in order to seize more job opportunities. They have to be proficient in performing EKGs and using the Holter monitor.
The Holter monitoring device is a wearable gadget that registers the patient’s heart activity for one or two days. The procedure allows a more accurate reading of the heart in case the EKG analysis is considered insufficient.
Furthermore, a certified EKG technician CET must be able to:
- Guide the patients through medical procedures;
- Execute cardiovascular exams and graphic diagnosis;
- Monitor pulse and blood pressure;
- Execute cardiopulmonary resuscitation and basic life support;
- Recognize cardiac abnormalities such as chest pain, tachycardia, arrhythmias, syncope, ventricular fibrillation, and other atypical vital signs;
- Perform stress tests and EKG strip analysis;
- Collect data through various ambulatory monitoring equipment such as the Holter device or pacemakers;
- Bookkeep patient records through Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Electronic Medical Records (EMR) software;
- Front office and back office administration;
- Perform maintenance, troubleshooting, and report malfunction;
- Adhere to safety regulations and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) confidentiality plans;
- Adhere to infection control methods such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA);
- Adhere to ethical standards such as the NHA Code of Ethics.
Education and Training
Considering that EKG is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure, there’s no legal requirement for formal education or training program.
However, the patient care industry strongly prefers standardized technicians as to avoid litigious actions or malpractice. Although the margin of error is smaller than that of invasive procedures, employers are not usually willing to take the risk of working with an uncertified technician. Patients have their rights reserved to sue medical practitioners, and because of this, clinics prefer hiring certified workers who completed at least one official training program.
In any case, the minimum required education is a high school diploma or equivalent GED. Certifications are available from several boarding institutions and guarantee adequate practical and theoretical preparation. Classes include the fundamental principles of electrophysiology and electrocardiographic methods and devices, clinical problem-solving, ECG reading, recognition of abnormalities such as arrhythmia and tachycardia, first aid, and pharmacology.
Several institutions across the U.S. offer training and certification. The most renowned certification institutions are:
- Cardiovascular Credentialing International (CCI);
- American Certification Agency for Healthcare Professionals (ACA);
- American Society of Phlebotomy Technicians (ASPT);
- National Healthcareer Association (NHA).
Certification
CET & Other Equivalent Acronyms
Both EKG and ECG refer to the same thing and mean electrocardiogram or electrocardiograph. The acronym EKG is primarily preferred because the equivalent ECG is usually mistaken for EEG, which means electroencephalogram, a similar analysis involving the brain.
Furthermore, the EKG technician is regularly abbreviated as CET. Other names and acronyms of the same position are Certified Cardiographic Technician (CCT), Cardiographic Technician (CGT), Cardiac Monitor Technician (CMT), Rhythm Analysis Technician (RAT), or Telemetry Monitor Technician (TMT).
Different institutions offer different certification training, but the vast majority of certifications hold basic equivalency in the work field. Having an official certified EKG technician CET documentation increases the chances of employment.
1. Cardiovascular Credentialing International (CCI):
The Cardiovascular Credentialing International (CCI) issuing organization is offering a CCT certificate and training for a fee of $170. The exam has 130 questions in two hours. It requires re-certification every three years for a cost of $150. It has more than 200 approved testing centers in the U.S. and 3000 international sites.
More information on the official CCI website and at (800) 326-0268.
2. American Certification Agency for Healthcare Professionals (ACA):
The American Certification Agency for Healthcare Professionals (ACA) boarding institution awards an EKG certification and training for an application fee of $100 and a test fee of $100. The exam is to be completed in two hours. It requires re-certification every two years for $80. The candidate must have a high school diploma with six months of EKG experience.
More information on the official ACA website and at 574-254-1307.
3. American Society of Phlebotomy Technicians (ASPT):
The American Society of Phlebotomy Technicians (ASPT) certification entity grants EKG certification and training for $80 with a 30-day advance, $110 with less than 30 days advance, or $130 with no days in advance. The exam lasts two hours. Eligible candidates must be ASPT members with six months of experience in performing EKG or be graduates from an EKG program.
More information on the official ASPT website and at 828-327-3000.
4. National Healthcareer Association (NHA):
The National Healthcareer Association (NHA) accrediting board is offering an EKG certification and training for $117. The exam is composed of 110 questions in two hours. Re-certification is required every two years for a fee of $169. With more than 550 U.S. testing sites, eligible candidates must have at least ten hours of experience performing EKGs on patients.
More information on the official NHA website and at (800) 499-9092.
5. American Society of EKG Technicians (ASET):
The American Society of EKG Technicians (ASET) certification program is awarding an EKG tech accreditation through its e-learning platform for an exam fee of $150. The price includes study material and unlimited test simulations. The candidate has three final attempts to pass the exam. Re-certification is required after two years for a fee of $100. More so, the agency has one of the largest job networks and will assist the graduate in finding work.
More info on the official ASET website and at (888) 797-9354.
Known Scams
National Phlebotomy Credentialing Excellence (NPCE)
OR
National Phlebotomy Credentialing Examination (NPCE)
NPCE.org offers EKG & Phlebotomy Certifications on their website. NPCE offers all of the same programs a real agency would, and always have the best price. The business appears to be a professional agency at glance. NPCE.org provides all of their study materials & exams online. They use this elaborate scheme to charge people for certifications that are not accepted, and are not nationally recognized.
NPCE states to be the only California approved Phlebotomy program in multiple places online. California does not recognize nor accept NPCE certifications, nor as a provider of Continuing Education in any capacity.
NPCE.org has been barred by every credentialing agency within the medical community. There have been numerous complaints filed against the company that go back to 2011. Electrocardiogram technicians beware.
Salary
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median salary of an EKG technician is $56,850 ($27.33 per hour). The EKG patient care job outlook is expected to grow by 22% through 2024.
The top-paying U.S. states for this occupation are:
- District of Columbia has an annual mean salary of $80,840 ($38.86 per hour);
- Oregon with $77,680 ($37.34 per hour);
- Massachusetts with $77,520 ($37.27 per hour);
- Connecticut with $76,800 ($36.92 per hour);
- New Jersey with $75,130 ($36.12 per hour)
The U.S. states with the largest employment level are:
- Texas has an annual mean salary of $54,550 ($26.23);
- California with $72,960 ($35.08);
- Florida with $49,340 ($23.72);
- New York with $63,690 ($30.62);
- Pennsylvania with $55,520 ($26.69).
The U.S. states with the largest job concentration are:
- Rhode Island has an annual mean salary of $73,380 ($35.28 per hour);
- West Virginia with $35,660 ($17.15 per hour);
- Delaware with $57,740 ($27.76 per hour);
- Michigan with $57,760 ($27.77 per hour);
- Kentucky with $49,370 ($23.73 per hour).